1.Meningioma

Roughly one-third of primary brain tumors are meningiomas. They are usually benign and slow growing.
They grow from tissue covering the brain and spinal cord and create pressure on these areas.
Meningiomas are rare in children and most common in women over the age of 60.
Symptoms of meningioma can include:
- headaches
- weakness in the arm or leg
- seizures
- changes in personality
- vision problems
2. Glioblastoma
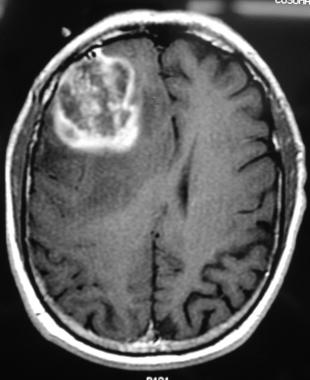
Glioblastomas are malignant tumors. They can be fast growing and require more intensive treatment.
According to the American Brain Tumor Association, healthcare providers assign a grade to tumors depending on how abnormal the cells they contain are.
Grade 1 tumors are the least malignant and grade 4 are the most malignant. Glioblastomas are grade 4 tumors.
Glioblastomas create pressure on the brain, and symptoms include:
- nausea and vomiting
- headaches, which may be more intense in the morning
- weakness in the body, such as in an arm, a leg, or the face
- difficulty balancing
- problems with memory
- seizures
3.Astrocytoma
Astrocytomas are brain tumors that grow from cells called astrocytes, which make up brain tissue.
They can range from grade 1 to 4, with grade 1 tumors being slower growing than grade 4 tumors.
Some of the early symptoms for astrocytoma include:
- headaches
- memory loss
- seizures
- changes in behavior
4.Craniopharyngioma

A craniopharyngioma is a benign tumor that develops close to the pituitary gland. It is much more common in children than adults. Medulloblastoma and ependymomas are also more common among children.
The tumor creates pressure on the pituitary gland and optic tract, which is an extension of the optic nerve. This can cause the following symptoms:
- delay in development
- obesity
- vision problems due to a swollen optic nerve
- hormone problems
5.Pituitary tumors

Pituitary tumors develop in the pituitary gland and affect hormone levels. They tend to be more common in women and make up 9–12% of all primary brain tumors.
They are slow growing, though larger tumors can create pressure on surrounding areas of the brain. These tumors can secrete pituitary hormones and cause additional symptoms.
According to the American Cancer Society, tumors that start in the pituitary gland are almost always noncancerous.
Symptoms of pituitary tumors include:
- headaches
- vision problems
- changes in behavior
- changes in hormone levels
6.Metastatic

Metastatic brain tumors, or secondary brain tumors, form in other parts of the body where cancer is present and move to the brain through the bloodstream.
Metastatic brain tumors present the same symptoms as primary brain tumors, with the most common symptoms being:
- headaches
- seizures
- short term memory loss
- changes in personality or behavior
- weakness on one side of the body
- balance difficulties
Read more about brain tumors:
2. Types and symptomes of every type
3. Cause
4. Diagnostics
5. Teatments


5 Comments