Treatment for a brain tumor differs depending on several factors: a person’s age, general health, and the size, location, and type of tumor.
You and your loved ones will have many questions about brain cancer, the treatment, side effects, and the long-term outlook. Your health care team is the best source of this information. Don’t hesitate to ask.
Brain Cancer Treatment Overview
Treatment of brain cancer is usually complex. Most treatment plans involve several consulting doctors.
- The team of doctors includes neurosurgeons (specialists in the brain and nervous system), oncologists, radiation oncologists (doctors who practice radiation therapy), and, of course, your primary health care provider. Your team may also include a dietitian, a social worker, a physical therapist, and, possibly, other specialists such as a neurologist.
- The treatment protocols vary widely according to the location of the tumor, its size and type, your age, and any additional medical problems that you may have.
- The most widely used treatments are surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. In most cases, more than one of these is used.
Brain Cancer Surgery

Many people with a brain tumor undergo surgery.
- The purpose of surgery is to confirm that the abnormality seen during testing is indeed a tumor and to remove the tumor. If the tumor cannot be removed, the surgeon will take a sample of the tumor to identify its type.
- In some cases, mostly in benign tumors, symptoms can be completely cured by surgical removal of the tumor. The neurosurgeon will attempt to remove all the tumor when possible.
You may undergo several treatments and procedures before surgery. For example:
- ou may be given a steroid drug, such as dexamethasone (Decadron), to relieve swelling.
- You may be treated with an anticonvulsant drug to relieve or prevent seizures.
- If you have excess cerebrospinal fluid collecting around the brain, a thin, plastic tube called a shunt may be placed to drain the fluid. One end of the shunt is placed in the cavity where fluid collects; the other end is threaded under your skin to another part of the body. The fluid drains from the brain to a site from which the fluid can be easily eliminated.
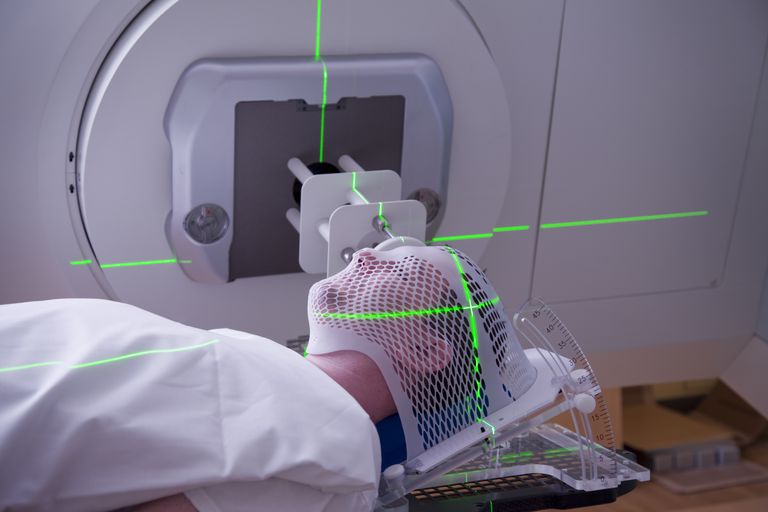
Radiation Therapy for Brain Cancer

Radiation therapy (also called radiotherapy) is the use of high-energy rays to kills tumor cells, thereby stopping them from growing and multiplying.
- Radiation therapy may be used for people who cannot undergo surgery. In other cases, it is used after surgery to kill any tumor cells that may remain.
- Radiation therapy is a local therapy. This means that it affects only cells in its path. It typically does not harm cells elsewhere in the body or even elsewhere in the brain.
Chemotherapy for Brain Cancer
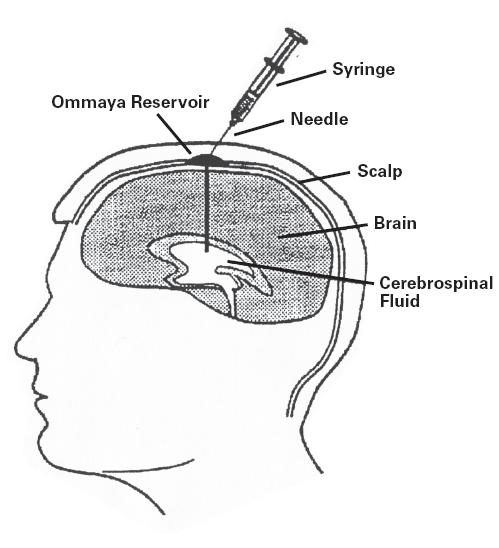
Chemotherapy is the use of powerful drugs to kill tumor cells.
- A single drug or a combination of drugs may be used.
- The drugs are given by mouth or through an IV line. Some medications are given through the shunt put in place to drain excess fluid from the brain.
- Chemotherapy is usually given in cycles. A cycle consists of a short period of intensive treatment followed by a period of rest and recovery. Each cycle lasts a few weeks.
- Most regimens are designed so that two to four cycles are completed. There is then a break in the treatment to see how your tumor has responded to the therapy.
- The side effects of chemotherapy are well known. They may be very difficult to tolerate for some people. They may include nausea and vomiting, mouth sores, loss of appetite, loss of hair, among others. Some of these side effects can be relieved or improved by medication.
New Brain Cancer Treatments
New therapies for cancer are being developed all the time. When a therapy shows promise, it is studied in a lab and improved as much as possible. It is then tested in clinical trials involving people with cancer.
Through brain cancer clinical trials, researchers test the effects of new medications on a group of volunteers with brain cancer. Patients with brain cancer may be reluctant to take part in clinical trials for fear of getting no treatment at all for their brain cancer.
- Clinical trials are available for virtually every kind of cancer.
- The advantage of clinical trials is that they offer new therapies that may be more effective than existing therapies or have fewer side effects.
- The disadvantage is that the therapy has not been proven to work or may not work in everyone.
- Many people with cancer are eligible for participation in clinical trials.
- To find out more, ask your oncologist. A list of clinical trials is available at the web site of the National Cancer Institute.
Read more about brain tumors:
2. Types and symptomes of every type
3. Cause
4. Diagnostics
5. Teatments

5 Comments